 ---SENKU MACHINERY
---SENKU MACHINERY
Why Need Temperature Sensor in the EV Charging Connectors?
In order to prevent high temperature risk during electric vehicle charging, it is request the high output current (Generally ≥ 60A) charging system to detect the EV charging connectors (EV plug or EV socket) temperature in real time, and when the EV connector temperature reach the over-temperature value, the charging system will derate the output power or shut down the charging process. Both EV charging station and Electric vehicle have such temperature detection systems.
For example:The following is a 250A CCS2 EV DC plug wire drawing:

We can see, the CCS2 plug power contacts DC+ and DC- with PT1000 temperature sensor, and each PT1000 with 2 wires, here we call it them T1, T2, T3 and T4;
T1 and T2 use to detect DC+ power contact of CCS2 plug
T3 and T4 use to detect DC- power contact of CCS2 plug
Working Principle of PT1000 Sensor
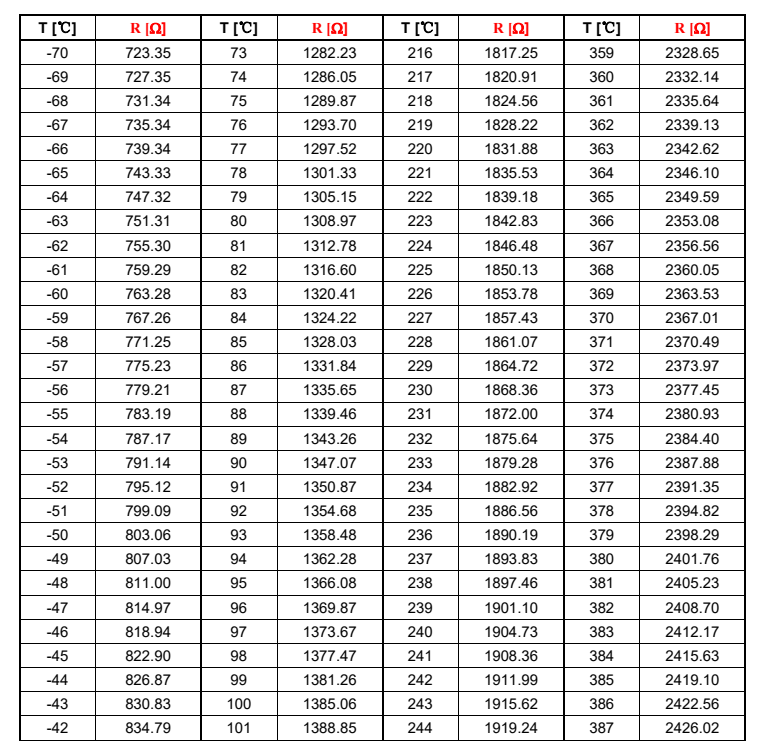
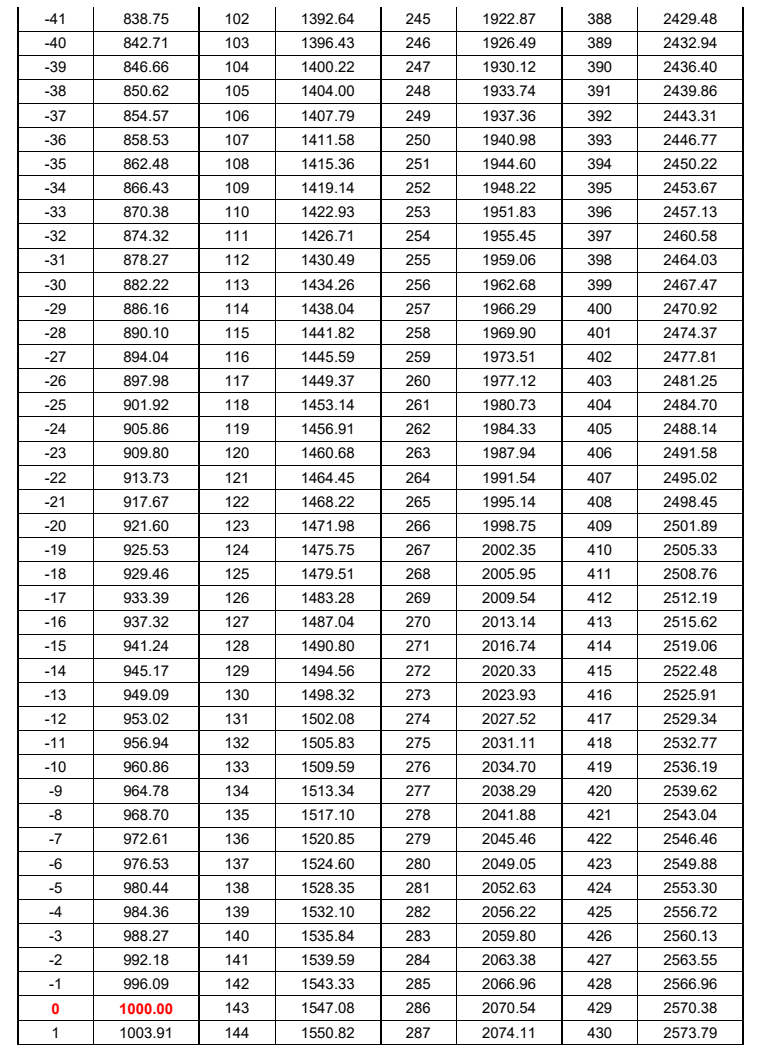
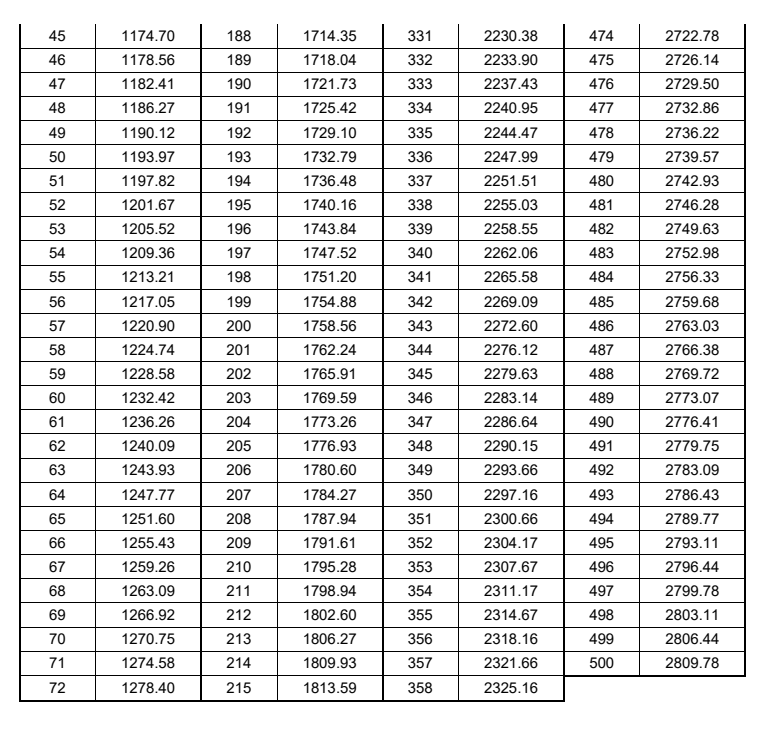
The resistance of PT1000 varies with temperature. The resistance value of PT1000 will increase with the increase of temperature, that is, the resistance is proportional to the temperature (please refer to the PT1000 resistance and temperature table at the end of the article).
Then, the wire sends the PT1000 resistance value to the charging station system. When the temperature is too high, you want to get an NC or NO signal, which is entirely up to you. for example
When the temperature is 0°C, the PT 1000 resistance value is 1000Ω:
If set the resistance value to a maximum of 1000Ω, If below 1000Ω, the signal is NO, and when the resistance value is greater than 1000Ω, the system will obtain an NC signal.
On the contrary, If set the resistance value to a maximum of 1000Ω, If below 1000Ω, the signal is NC, and when the resistance value is greater than 1000Ω, the system will obtain an NO signal.
Note:
*The above values are for reference only.
*You can set the maximum resistance value according to system requirements.
PT1000 Resistance and Temperature Table

Tags: #pt1000 #ev charging connector #ccs plug



 Senku ,Bake
Senku ,Bake Senku
Senku